Lewis dot Structure of H2S
The chemistry graduates often encounter the hydrogen sulfide molecule due to the wide range of industrial applications. If we look into the formation of hydrogen sulfide molecules only two bonds of H-S contribute to the stable and accurate molecular structure. Are you here to find out the lewis structure of h2s? You have to identify the number of valence electrons in the h2s molecule. The structure of the h2s is relatively stable due to the formation of sulfur hydrogen bonds and the mutual sharing of electrons.
Hydrogen sulfide is widely applicable as a precursor in inorganic metal ions compounds. The h2s compound is formed by various laboratory chemical reactions and comprises only two elements hydrogens and sulfur. The researchers have found that h2s have a pivotal role in the cell signalling pathway in living organisms. The other benefit of h2s is that it was one of the core compounds used in aerobic bacteria when there weren’t any sufficient oxygen molecules present. On the contrary, the hybridization of the h2s is sp3 with a single p orbital mixing with 3 p orbitals to give sp3 hybridization.
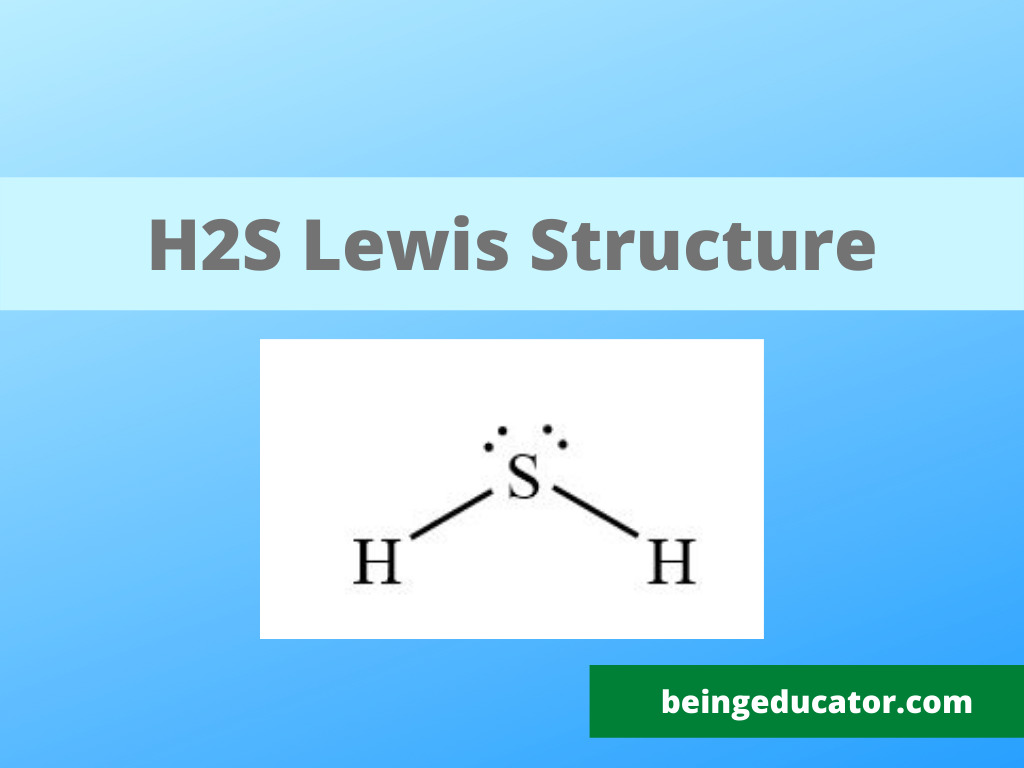
The chemical compounds are very predictable depending on the valence electron for the correct interpretation of their lewis structure. You may ask what the core importance of the lewis structure is. In my opinion, the lewis structure has its benefits, including structure prediction, helping in molecular geometry, bond to bond interaction, and predicting the polar nature of compounds.
The formation of the compound has many implications in the molecular geometry and deciphering the molecule’s structure.
Steps of Calculating the lewis structure of H2S
The periodic table gives the arrangement of elements in order of their increasing atomic number and helps us study the properties of elements. The elements with similar properties are placed in the same group. The trend of various chemical properties like electronegativity, atomic shell, electron affinity has a similar pattern across the groups and periods. Suppose you are here to know the lewis structure of any molecule. In that case, the periodic table can be a real game-changer because it not only tells us about the atomic size but also tells about the valence electrons.
The first step is the knowledge about the valence electrons, and the sulfur atom has six valence electrons while hydrogen has one valence electron. The total valence electrons in h2s are 8.
The following rule is to find out the central atom to predict the lewis structure, and it helps in predicting the stable diagrammatic representation of any molecule. A question may arise in your mind about the definition of lewis structure. Lewis structure is a 2D diagram of atoms participating in the bonding with the information of bond pair, lone pair, and formal charge on the atoms. The lewis structure diagram is beneficial in chemistry because it gives a correct structure and aids in determining the molecule’s shape.
The dots represent the electrons, and most of the compounds follow the octet rule. The octet rule is the attaining of the electronic configuration of the molecules with the nearest noble gas. Group 18 of the periodic table are the noble gases (rare gases) with the unique property of having complete valence electrons. They are thought to be more stable elements among the other elements.
The second step is to find out the central atom and the more stable variation is the sulfur in the middle of two hydrogen atoms. The octet rule and the shape are predicted correctly only if the sulfur is in the centre.
Now it is time for electron distribution, and in this case, we have to follow the octet rule. The hydrogen molecule shares one electron with sulfur, and the octet of both is fulfilled. The two lone pairs of electrons remained on the sulfur atom and are placed in the dot format. The straight lines are used to represent the single bond between the bonded atoms.
H2S Hybridization
The data from VESPER theory and VESPER Chart Reveals that the H2S molecule has no hybridization because of no mixing of orbitals. You can see more NH3 Polar or Non Polar
H2S Molecular Geometry
The shape and molecular geometry of the H2S molecule are tetrahedral and the bond angle of the H-S bond is 92.1 with a bond length of 133.6pm.
H2S Polar or Non Polar
The H2S molecule is polar due to the bent shape of the molecule. The other logical explanation of the polarity of the H2S molecule is that the bonding molecules do not cancel each other dipoles and the molecule has a net dipole moment making it one of the polar molecules.