PCl3 Polar or Non Polar
Most of us think that the compounds of Phosphorus are flammable and require proper handling to operate. Today, we will discuss is pcl3 polar or nonpolar, and the compound PCl3 named phosphorus trichloride is a pungent-smelling liquid that shows polar behavior.
Have you wondered that the PCl3 has a pungent smell, just like the hydrogen chloride? Phosphorus trichloride PCl3 is a toxic fumy liquid, when reacted with water, yields HCl, a polar compound with tetrahedral geometry. When you study the polarity chapter in your chemistry lesson, you will be taught about the pcl3. After your lecture, many students confuse about whether pcl3 is polar or nonpolar. In this blog post, we will discuss in detail the polar nature of pcl3.
The phosphorus trichloride is formed in the industries when the white phosphorus is reacted with chlorine in the presence of PCl3 as a solvent. The PCl3 is a polar molecule, and the polarity is due to its tetrahedral geometry with a lone pair of electrons on the phosphorus atom. The electronegativity difference between chlorine and phosphorus creates two opposing dipoles with a more negative charge on chlorine and a positive charge on phosphorus results in polar bond formation.
There are three chlorine atoms bonded with phosphorus with a single covalent bond, and only one lone pair of electrons on the phosphorus gives tetrahedral geometry to the pcl3 molecule. Chlorine belongs to the family of halogen with the oxidation state of -1 and phosphorus is one of transition metal have an oxidation state of +3
PCl3 bond angle
The bond angle of PCl3 is 103 and shows the tetrahedral geometry.
PCl3 hybridization
The pcl3 molecule shows sp3 hybridization where one s and three p orbitals bond together to give a tetrahedral geometry.
PCl3 dipole moment
Most of the chemistry students make a comparison that the blc3 dont have dipole moment but pcl3 have a dipole moment. The reason is the molecular geometry because the former one (bcl3) has a symmetric confirmation but later(pcl3) is not symmetric. The other logical explanation is that there is one lone pair of electrons on pcl3 and the other 3 bonded pairs are also present on the pcl3 molecule.
PCl3 polarity
The tetrahedral configuration and the electronegativity difference make the pcl3 molecule among the polar compounds. Chlorine belongs to the group of elements called halogens(Salt-Forming) and halogens are among those elements with high electronegative elements. When two molecules with electronegativity difference bond together the difference creates two opposing dipoles and results in the formation of polar bonds. An important thing to consider is that the polar bond can be ionic as well as covalent.
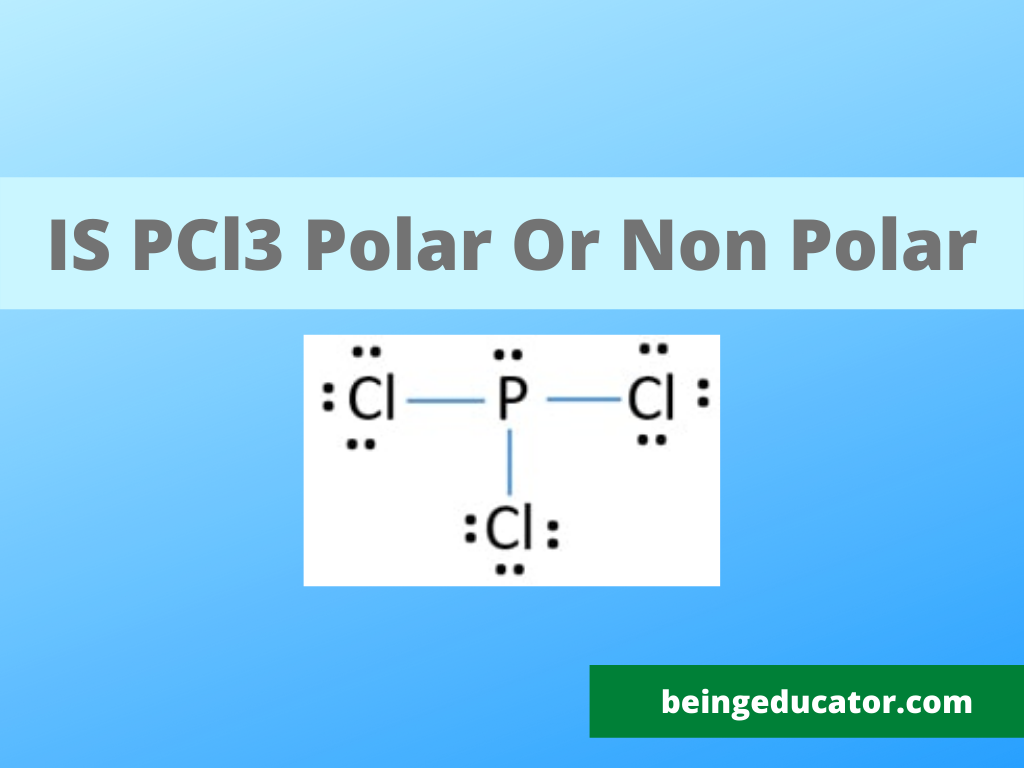
PCl3 Lewis Structure
PCl3 is made of two atoms group VA Phosphorus and chlorine from the halogen family. The phosphorus has three valence electrons, and chlorine has seven valence electrons. The three chlorine atoms bonds with phosphorus and 26 valence electrons are present in the PCl3 compound.
What kind of bond is pcl3?
If we look at the chemistry of pcl3, the polar bond is present between the chlorine and phosphorus atoms. The logical explanation for the presence of polar bonds is due to the electronegativity difference between both bonding atoms and the lone pair of electrons on the phosphorus atom.
Uses of PCl3
Pcl3 exists in the liquid physical state at room temperature and is one of the raw materials for manufacturing phosphites, insecticides, and pesticides.
Conclusion
If you are looking for the answer “is pcl3 polar or nonpolar”, the answer is pcl3 is a polar compound and shows tetrahedral symmetry. The difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms and the lone pair of electron on the phosphorus creates two opposing dipoles and make the pcl3 a polar compound.