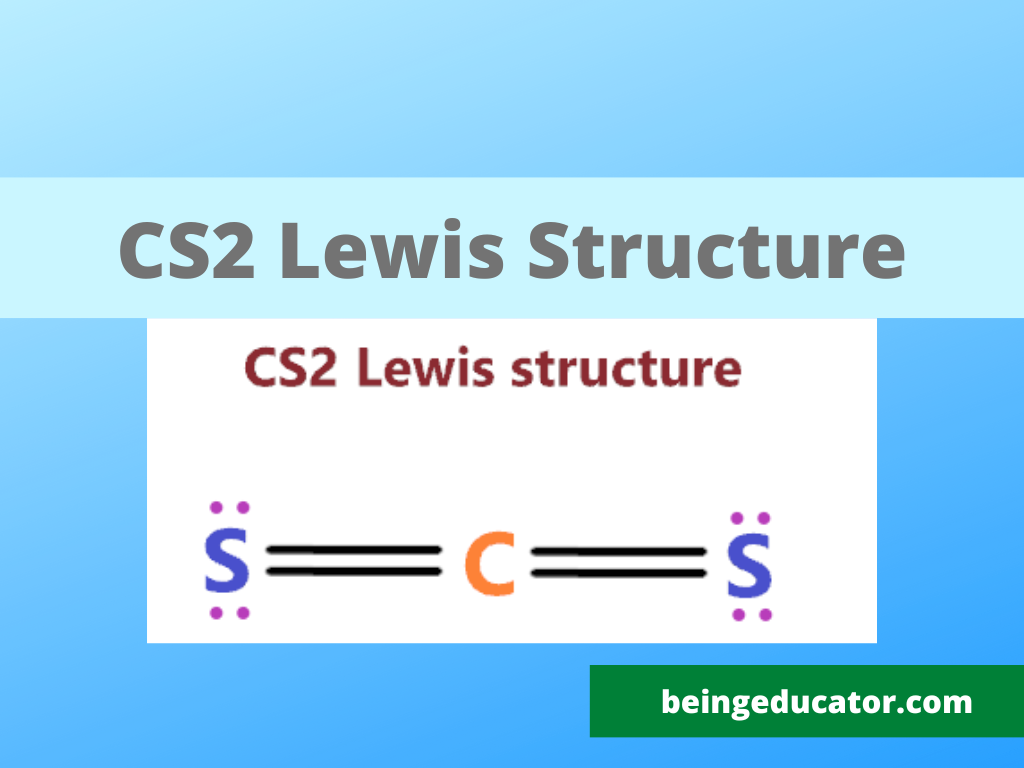
CS2 Lewis Structure
The interesting thing while studying inorganic compounds is that you need to study the raw materials involves in the formation of chemical compounds.CS2 is a very handy inorganic compound and chiefly it is used as a raw material in the preparation of carbon tetra chloride. Carbon disulfide is a very dangerous compound when it comes to contact with human beings the real thing is it causes several diseases. In this topic, we are going to discuss the cs2 lewis structure in detail.
Carbon Disulphide is a triatomic molecule and two sulphur and one carbon atom are present in it. The CS2 is a very volatile liquid and human contact can be a real danger as it causes several ailments in humans. If you are looking for cs2 lewis structure, molecular geometry, hybridization and polarity I am going to explain the step-by-step guide with an explanation. The non-polar nature of cs2 gives an easier hint of its solubility in non-polar solvents including benzene, ether etc. The usability of carbon disulfide ranges from soil disinfection and eradicating pests to increasing crop yields.
What is lewis structure?
A lewis structure is an actual way how the shape of a molecule is explained with the help of valence electrons. Despite this fact, many students fail to understand the most important factor in chemical bonding which is how electrons in the last shell behave. So in general lewis structure is the 3D explanation of the shape of a molecule.
A lewis dot structure is usually explained by the dots between the atoms. These dots are the electrons. The bonding electrons are shown as a single line and non-bonding electrons as dots. The octet rule principle is followed while writing the lewis structure of any element, molecule, ion or compound.
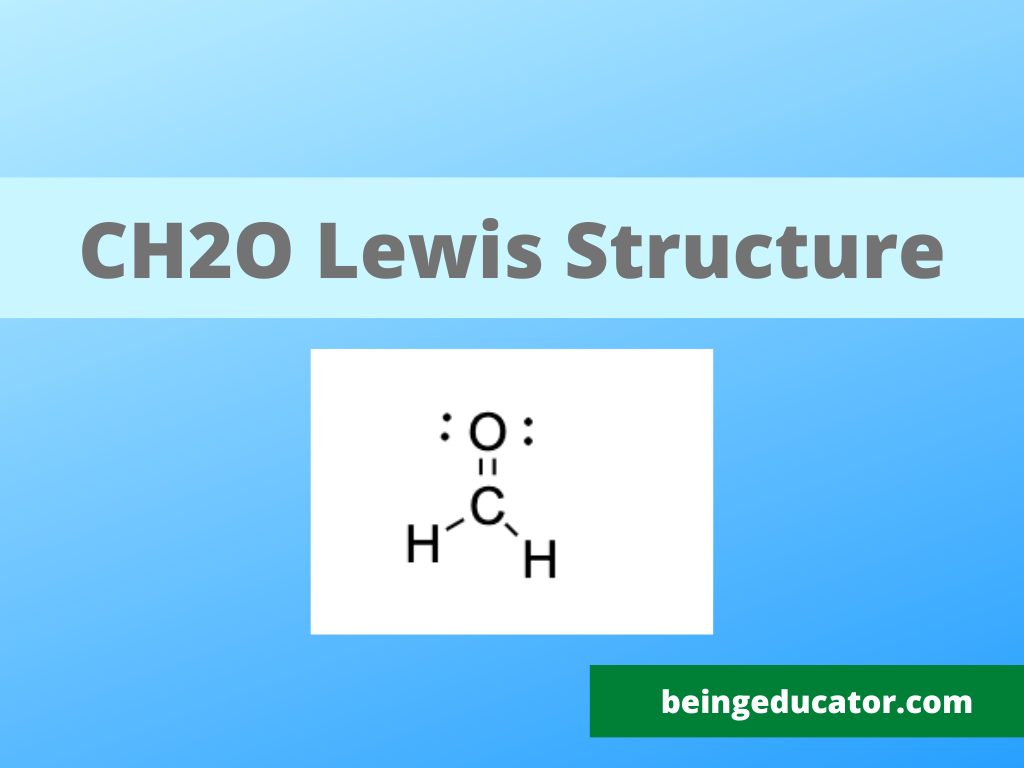
You can check the CH2O Lewis Structure explained step by step. The method to calculate the valence electrons, molecular geometry, hybridization and polarity of CH2O is discussed in detail.
Steps of Writing Lewis Structure of Carbon Di Sulfide
The promising thing about cs2 is that it is a very common compound that shows a linear shape. The importance of knowing the lewis structure of cs2 can be known as in many exams students are asked to draw the lewis stricter of cs2.
Step 1
The first step where students make mistakes is to calculate the wrong valence electrons. The valance electrons of any particular compound can be calculated by the sum of valence electrons of the bonding atom, In the case of cs2 we have one carbon and two sulfur atoms and in carbon, there are four valence electrons and in the sulfur present the 6. Thus a total of sixteen valence electrons are present in the CS2 atom.
2×6+1×4=12+4=16
Step 2
Now you have to choose the central atom and the atom with the least electronegative value comes in a central position. In Carbon disulfide carbon electronegativity is slightly less than sulfur thus carbon will be in the centre of the cs2 lewis structure with a sulfur atom on the side.
Step 3
Now the position of atoms is set based on their electronegative values then place the bonds between carbon and sulfur. Firstly fulfil the octet of the outer atoms. Then move towards the central atoms. A single bond comprises two electrons thus two single covalent bonds between carbon and sulfur exist. Of 16 valence electrons, only four involved in the formation of chemical bonds and 12 electrons valence electrons are still needed attention.
Step 4
12 valence electrons are required are still remaining for the carbon disulfide atom. Seeing the structure of the cs2 the 3 lone pairs of electrons are placed on the dots on the sulfur atoms. An atom follows octet rules only when each atom has 8 electrons in the valence electrons.
In order to complete the octet of carbon, the electron pair from each sulfur is shared with the carbon resulting in a carbon-sulfur double bond.
Step 5
The final step is the calculation of the formal charge on the cs2. The net formal charge on any atom exists due to the difference in the dipole moment of both atoms. In CS2 the net charge is zero resulting in the stable form of carbon di sulfide.
Hybridization of CS2
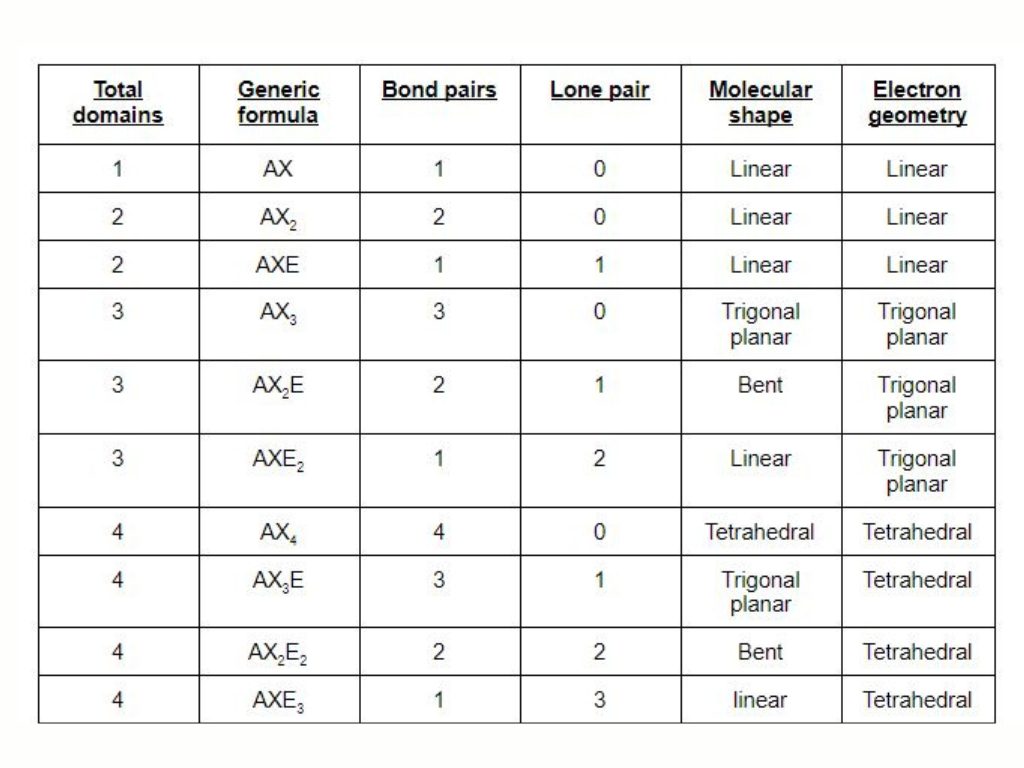
The concept of hybridization has a direct correlation with the steric number. If you want to know the hybridization of carbon disulfide, the steric number comes real handy. A steric number is based on the presence of lone pair on the central atom and the number of atoms that make the bond with it. In carbon disulfide, there is no lone pair on the carbon atom and it makes two bonds with both sulfur atoms. Thus the -carbon disulfide has steric number=0+2=2.
Thus CS2 shows sp hybridization. The one s orbital and one p orbital mix gives rise to the sp hybridization. The hybridization of cs2 is explained by VSEPR theory.
Polarity of CS2
A dipole moment on any particular atom redefines its polar nature. If the net dipole moment on any atom is not equal to zero, it shows the existence of polarity on it. Thus a molecule with a net dipole moment equal to zero shows non-polar behaviour.
Is CS2 Polar or Non-Polar? Carbon disulfide is a non-polar molecule due to its linear shape. The electronic charge on both sulfur atoms cancels each other resulting in net dipole moment zero making cs2 a non-polar molecule.
Molecular Geometry of CS2
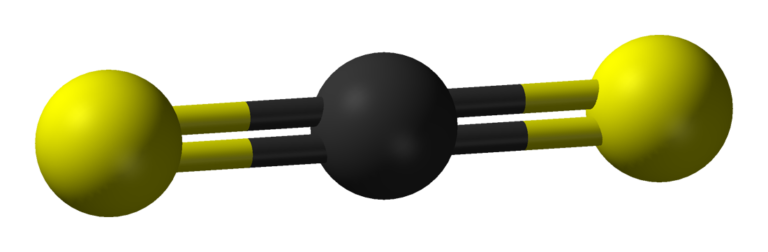
The sp hybridization in the CS2 molecules clearly shows the linear geometry. The linear geometry or shape predicts the bond angle of the bonding atoms which is 180. So the shape of CS2 is linear with a C-S bond angle of 180.
Summary
Carbon disulfide is a highly volatile and toxic liquid and is utilized in some industrial processes. The nature of cs2 is non-polar due to the symmetric behaviour shown by both sulfur atoms. The molecular geometry of cs2 is linear with a bond angle of 180. The carbon-sulfur double bond helps in fulfilling the octet of the central atom, The CS2 Lewis structure requires a series of steps including calculating the valence electrons and determining the central atom and distribution of net charge on it.